Smart Manufacturing: The Anatomy of It
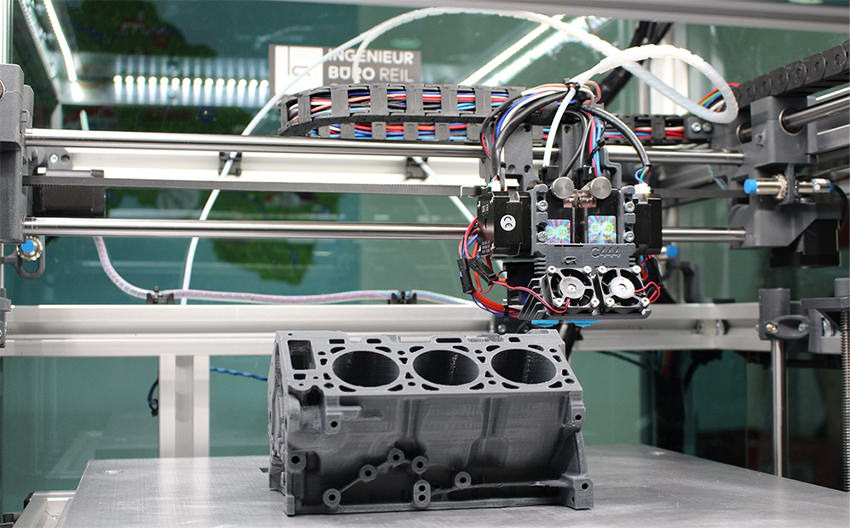
Smart Manufacturing is the current inclination and interest in manufacturing industries right now. It is explicated and defined as a broad category of manufacturing with the goal of optimizing, nurturing and augmenting the manufacturing process altogether.
Smart manufacturing is the process that employs machines with technologies. It is a collaboration of computer control mechanics, data modeling, upgraded digitalization, and other automation to improve manufacturing efficiencies.
Smart manufacturing also aims to take benefit of advanced information, communication, expertise, and manufacturing technologies to enable flexibility, feasibility in physical labor processes to address a dynamic, versatile and global market.
Smart manufacturing also aims to take benefit of advanced information, communication, expertise, and manufacturing technologies to enable flexibility, feasibility in physical labor processes to address a dynamic, versatile and global market.
“Smart Manufacturing is being predicted as the next Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0. And, as with many other advances throughout recent years, it all has to do with technology connectivity and the advances in the contextualization of data.”
In recent years, manufacturing has been theorized as a new and improved system that goes beyond the factory floors. It is believed to be encompassing the paradigms of “manufacturing as an ecosystem”. The term “smart” comprehends enterprises that create and use data and information throughout the product lifecycle to bring technologically improved products that fulfill the need of consumers.
The goal is to create and manage flexible manufacturing processes that respond rapidly to dynamic changes in demand and supply products at low cost to the firm without damage to the environment. The concept flourishes a life-cycle view, where products are designed with the help of digital advances for efficient production and recyclability.
The broad spectrum of smart manufacturing covers many different digital technologies. Some of the few key technologies in the smart manufacturing movement include big data processing capabilities, industrial connectivity devices and services, and advanced robotics.
a) Big data processing: Smart manufacturing utilizes big data analytics technique, to refine complicated processes, simplify stages and manage supply chains digitally. It refers to the technique of gathering and understanding large data sets in terms of what is known as the three V’s, velocity, variety, and volume. A simplified data regulates the ease of production and manages the throughput effectively. It permits an enterprise to use smart manufacturing theory to shift from traditional practices to prophetic ones, a change that targets forecasted approach that improves the efficiency of the manufacturing process and regulates the performance of the product.
b) Advanced robotics: Advanced robots as understood by its name are smart machines that operate autonomously and can communicate directly with manufacturing systems easily anywhere and at any time. The automatically advanced robots are equipped with features like problem-solving, decision making, initiate judgments and propagate communications too. These robots can complete work before time, error-free and are programmed with artificial intelligence that allows them to learn from experience and human-machine involvements.
c) Industrial connectivity devices and services: Taking advantage of the capabilities of the internet, manufacturers can increase integration and data storage affluently. IoT Application Development Company support digitally advanced technologies like machine learning, Big Data technology, and machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, adopting the sensor data, robotics, artificial intelligence and automation technologies.
The collaboration has evolved the segment to reduce cost and increase productivity simultaneously. The industries are well connected with highly configurable computing resources through the cloud. This gives the benefit of integrating servers, networks and other storage applications to be created, shared and released at a rapid pace.
Benefits and Aim of Smart Manufacturing:
a) Enhance workplace competencies: Smart manufacturing is about supporting employees and people involved do their jobs better. Integration of machines with physical labor addresses to challenges that no one foresees. For example, providing factory operators with machine advances that deliver healthy production; quality, insightful data allows them to act in real time basis to address backlog, errors, slowdowns or quality variances. Information delivery across channels becomes easier and thus increases the competencies of across the globe. This empowers the workers as well as the economy and enterprise associated with it.
Smart manufacturing brings a base for both machines and human simultaneously thus emphasizing on a smart workplace. It also encourages and attracts the younger, skilled and tech-savvy workforce into the industry. Utilizing smart manufacturing data and apps in the industry nurtures the employees to recognize new opportunities and eventually increases productivity.
b) Emerging trend: Smart manufacturing has introduced multiple new trends that benefit not only the industry but also the people involved with it. Various companies that provide digital services has enabled machinery in industries that can transmit operational information to the partners from one location to another in a matter of seconds like original equipment manufacturers and to field engineers.
Such instant information enables operation managers and factory heads to remotely manage the factory units without any fuss and take advantage of process automation and optimization. Along with this, Emerging trends allows big data to manage the throughput of the industry. A digitally connected unit/industry establishes a better line of commands thus enhancing decision-making capabilities tenuously and help identify key result areas (KRAs) for managers and workers.
c) Ensure sustainability: Every new trend promises to bring sustainability in the market. Smart manufacturing is not just a buzzword but has bought balance with the inclusion of digitization. Sustainability in the business means a balanced atmosphere of economic, social and environmental capability.
Smart manufacturing plays the cards right by achieving all three together, supplying the real-time data that is needed to capture opportunities, minimal costs, and high productivity. It prefers the better understanding of waste and material losses and monitoring the workforce challenges. A sustainable surrounding is achieved when companies gather the data needed to address issues of social responsibility, such as customer demands for the fair trade and work practices.
d) Bring profitability: In the end, it’s always about the profits! Technology is involved in the industry to cope with various challenges of backlogs, human errors, manage big data, improve productivity, supply services in decided time etc.
Smart manufacturing processes provide wide access to data across an entire supply chain network. It supports the workers to manage the task in real time basis and tweak as per the challenges arise. The instant decision-making supports makes things efficient for suppliers to easily make adjustments to orders. They supply what’s needed, not more or less, reducing waste and any downtime associated with missing parts hence improving profitability with each passing stage.
e) Agile and data-driven: The industry that is quick, responsive, and agile sustains in the market with technological turbulence. Competition is vicious and it does not let weak players sustain for long. With smart manufacturing processes, business leaders can make better-informed decisions. The introduction of the internet, big data, analytics and the cloud has made it easy for decision-makers to work on the agile environment throughout the company.
The data is no longer directed to just one single person, it can be shared with an intelligent machine that captures learning as things are happening. This process ensures notifying only that person who is required for the task and as & when necessary.
Data has shared power with the humans to connect technologies with manufacturing for faster information gathering, processing, communication, and remotely managing that in return enables faster decision making. Moreover, opportunities and problems are identified early and dealt quickly to support decision makers to respond to changes in the marketplace, whether global or local.
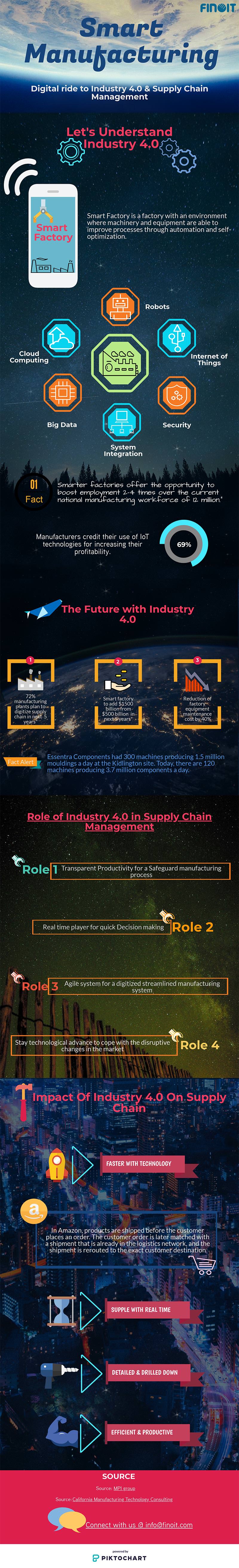
The infographic below explores about the future of manufacturing with Industry 4.0; it also explains what smart manufacturing is, and digital supply chain.
Related: Digital Supply Chain in Industry 4.0
Conclusion:
The manufacturing industry is competitive, and all companies are constantly seeking an edge at par to stay competitive to stay ahead. Feeble are not given chance to stay for long. It’s the power of agile industries that forecasts and plan strategy.
Technology changes with every trend. The one who addresses the change is the one that stays for longer. Every manufacturing industry wants to become more efficient, operate with greater profitability and serve customers the best. The same way smart manufacturing processes embrace the digital trend and provide a powerful set of mechanism that can deliver these advantages.
It takes the balance of emerging data and understanding of market needs that brings the output of best advantage over the others. The industry has to dive deeper into specific manufacturing segments and environments, yet at the same time not to forget the many overlapping and traditional evolutions across manufacturing to hit the market’s bull’s eye overall.
Finoit Technologies is a renowned mobile app development company providing custom software development services and IOT application development services. We have developed over 450 mobile apps, and have assisted many solopreneurs in their journey of startups by functioning as a tech partner and rolling out their product ideas. For questions/queries, you may write to us at info@finoit.com
